Stimulating domestic consumption
One of the "keys" to economic development in 2024 is to stimulate domestic demand in tandem with increased output, but numerous hurdles remain.

Consumer demand is the main GDP growth driver in the coming time. Photo: T. Nhan
>> Efforts to boost consumer demand at year’s end
Gaining momentum in 3Q23, with GDP growth of about 5.33% over the same period last year, with the service sector, particularly domestic consumption, accounting for 75-80% of GDP, Dr. Nguyen Quoc Viet - Deputy Director of the Institute for Research and Policy commented: consumer demand will be the main growth driver in the coming time, along with the spread of public investment packages, stimulus packages, exports...
Many economists share this view, emphasizing the importance of the home market in economic growth, particularly during tough periods characterized by detrimental and difficult-to-control economic effects of the global economy, as is the case today. The domestic consumer market is also regarded appealing for investment since the economy has a high marginal consumption propensity; domestic consumption spending accounts for approximately two-thirds of GDP, with household expenditure accounting for 50-55 percent of GDP. The massive population, which includes approximately 20 million middle-class residents, generates enormous consumer demand.
With the current problems, domestic spending stimulus is a significant driver of GDP growth and the major contributor spreading the fiscal multiplier in 2024. Especially when measures to boost consumption and local production contribute to activation and resonance effects from recently dispersed public investment money.
However, analyzing economic data in November, the World Bank Vietnam also pointed out some slowdowns in the domestic consumer market when purchasing power has not returned to excitement, especially compared to the pre-pandemic period. Specifically, Retail sales (a proxy for domestic consumption) registered - 0.27 percent (m/m, SA) in November 2023, following the 1.65 percent expansion (m/m, SA) registered in October. Picking up from the slump at 5.0 percent y/y (SA) in July 2023, retails sales growth has been relatively flat at around 7.5 percent y/y (SA) in between August and November, well below the prepandemic growth rates of about 12 percent y/y (SA).
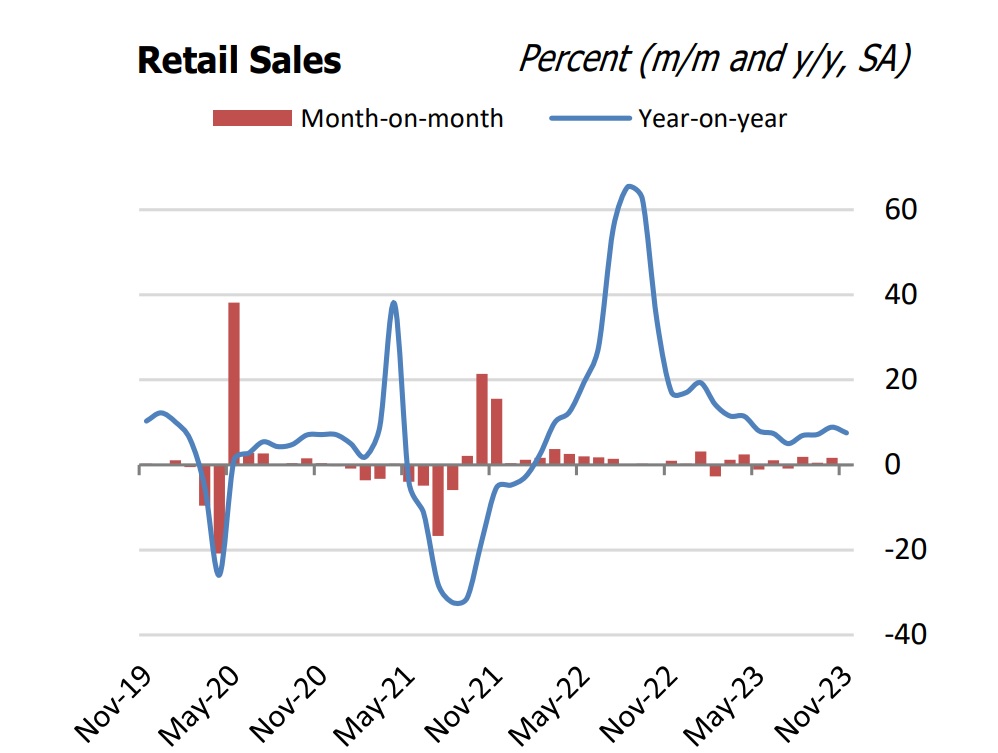
“The sales of goods, which account for almost 80 percent of total retail sales, was flat at -0.12 percent (m/m, SA), in November 2023 compared with -0.49 percent (m/m, SA) October. Meanwhile, sales of hospitality services contracted by 3.6 percent (m/m, SA) in November 2023, compared with contraction of 4.4 percent (m/m, SA) in October. Tourism services continued to contract at 11.2 percent (m/m, SA), 1.8 percentage point lower than a month earlier, reflecting weak domestic tourism”, said WB.
>> Does Vietnam still have room to stimulate consumer demand?
From the above data, the WB noted, Vietnam could consider extending the implementation of the economic support program (2022-2023) into next year to allow its planned investments to be fully implemented, supporting aggregate demand. Amid economic slowdown, financial sector vulnerabilities call for continued vigilance while efforts to restore confidence and promote a healthy development of the real estate markets will be key to supporting economic stability in the short term and economic growth in the long term.
Dr. Do Thien Anh Tuan, lecturer in Macroeconomics, Public Sector Economics and Financial Analysis, and Development Finance at the Fulbright School, emphasized the importance of encouraging consumption of Vietnamese goods through tax policies such as extending the VAT reduction period to create market motivation; strongly promoting reductions in corporate income tax and personal income tax have become obsolete.
Mr. Nguyen Anh Duc, Chairman of the Vietnam Retailers Association, stated that policies must be implemented more fundamentally in 2024 in order to produce a steady, long-term stimulus effect. It is critical, in particular, to increase direct support programs for businesses, such as lowering space leasing rates to stimulate the retail sales sector... Furthermore, because interest rates, the consumer price index (CPI), and foreign currency rates have a significant influence on the retail business, state authorities must implement faster-paced operational regulations in order to adapt to market movements.








