Outlook for the USD/VND exchange rate in 2026
MBS anticipates greater exchange rate stability in 2026, with the VND expected to depreciate by 2.5% - 3%.
In 2025, the US dollar recorded its sharpest decline in 8 years, falling 10.1% from the beginning of the year. On December 10, as widely anticipated by the market, the US Federal Reserve cut interest rates by another 25 bps—the third rate cut of the year—bringing the policy rate down to 3.5%–3.75%, the lowest level since November 2022.
Looking to 2026, the dot-plot chart indicates that Fed officials remain highly cautious, projecting only one additional rate cut next year amid stronger-than-expected economic growth, with Q3 GDP accelerating to a two-year high of 4.3%. Nevertheless, inflationary pressures persist, remaining stubbornly anchored above the 2% target.
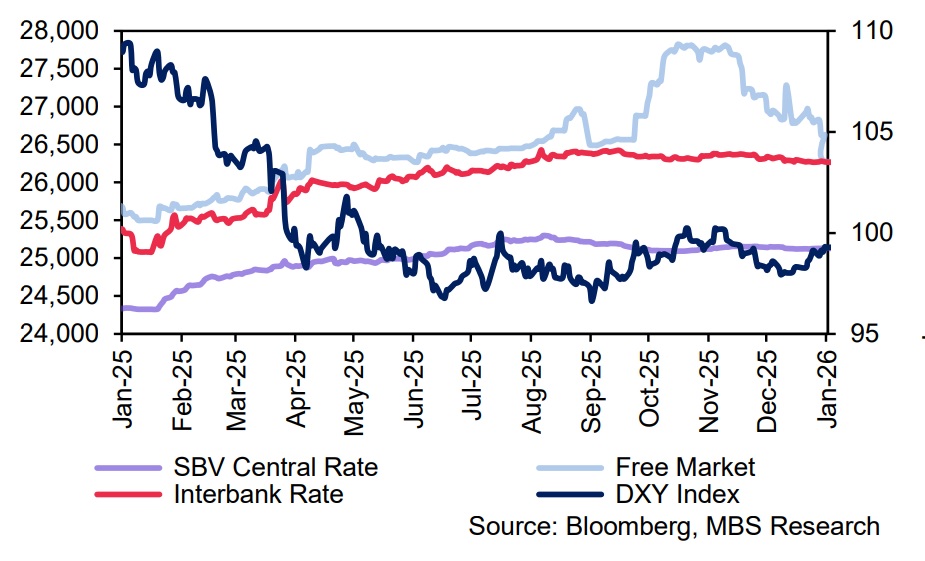
The USD/VND rate cooled significantly in December 2025. Specifically, the central rate and interbank rate stood at 25,121 VND/USD (3.2% ytd) and 26,297 VND/USD (3.3% ytd) by end-December 2025, respectively. Along with that, the free-market rate dropped sharply by 3.7% from its peak, closing the year at 26,785 VND/USD (4% ytd). Exchange rate pressure eased amid continued weakening of the USD following the Fed’s rate cuts.
In addition, the VND was supported by domestic factors: (1) The VND-USD interest rate gap remained positive, with the average interbank overnight rate anchored at 6%, compared to around 4% on average in the first 11 months of 2025. (2) Domestic USD supply was more abundant during the peak export season and the typical surge in remittances to Vietnam toward year-end.
In the first half of January 2026, the USD/VND rate remained relatively stable. The current interbank rate stands at 26,270 VND/USD—flat compared to the beginning of the year—while the free-market rate declined 1.1% ytd to 26,625 VND/USD. In contrast, the central rate edged up slightly by 0.03% to 25,131 VND/USD.
MBS believed that exchange rate pressures in 2026 will stem from the following: First, although Vietnam recorded a trade surplus of more than USD 20bn in 2025, the bulk of the surplus came from the FDI sector, while domestic enterprises posted a deficit of nearly USD 30bn, indicating persistently strong domestic USD demand during the production expansion cycle.
Second, it expects imports to grow in line with exports in 2026, mainly driven by increased imports from the US as Vietnam continues to narrow the trade deficit with this market.
Third, international gold prices are forecast to continue rising toward the 6,000 USD/ounce level due to geopolitical instability and heightened safe-haven demand from investors. Rising demand for gold imports will also exert pressure on the domestic exchange rate.
On the other hand, supporting factors for the exchange rate will primarily stem from the projected continued weakening of the USD, driven by monetary policy divergence among major economies. The DXY index is expected to fall to the 95 level from mid-2026, while most major currencies such as the Japanese Yen, British Pound, and EUR are anticipated to appreciate. Currencies of emerging economies, including the VND, are also expected to benefit as the interest rate differential between the US and these countries narrows. Balancing the above factors, MBS anticipates greater exchange rate stability in 2026, with the VND expected to depreciate by 2.5% - 3%.








